Nov 30, 2025

AI shopping agents are no longer speculative. They are actively reshaping how consumers search, compare, evaluate, and buy products online.
These are autonomous systems that interpret human intent, gather data, apply logical filters, and execute transactions on behalf of users. They do not scroll webpages or interpret visual design. They parse structured data, evaluate based on rules, and act quickly and programmatically.
Understanding how these agents make decisions is not a curiosity. It is a strategic imperative if your brand wants to remain visible, relevant, and competitive.
This guide breaks down how AI agents move from human prompts to purchases and what organizations must change to win in this new era.
1. The Journey Begins: Human Intent Becomes a Prompt
Every AI shopping journey starts with a human signal. It could be:
“Find a rugged laptop under $1,500 with 16GB RAM”
“Book a boutique hotel in Lisbon under $200 per night”
“Compare CRM tools for a 20-person team”
The agent takes that prompt, translates it into a structured task with constraints, and then builds a plan to fulfill it.
This is less like website search and more like delegating a mandate to a highly capable assistant.
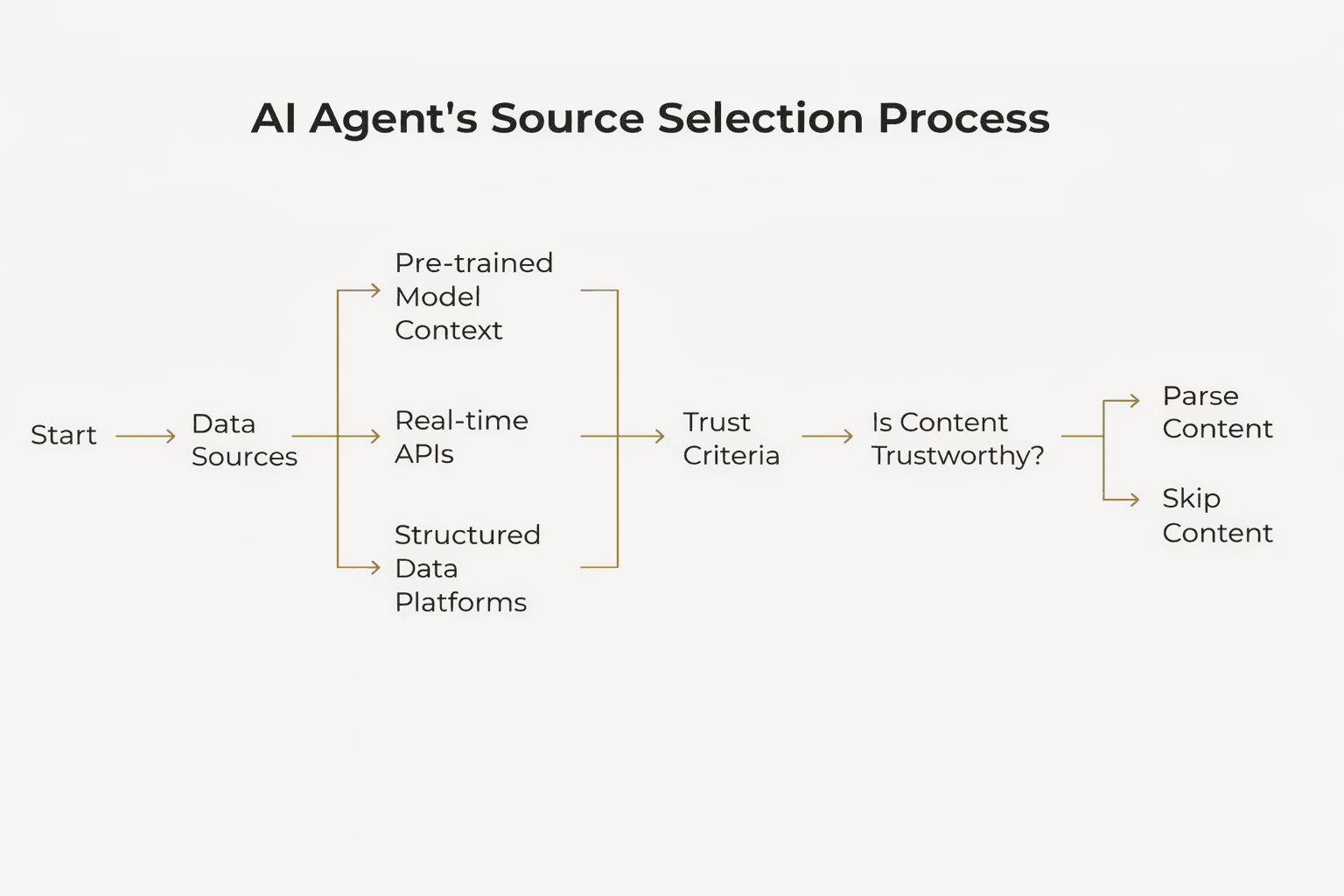
2. Source Selection: The Agent’s Discovery Phase
Unlike humans, agents do not rely on search result rankings or navigation menus. Instead, they:
Pull structured data from APIs, plugins, and feeds
Prefer machine-readable formats such as JSON-LD and schema.org
Trust sources with clear pricing, inventory, and verified metadata
If your product information is hidden behind JavaScript, lacks structured markup, or is inconsistent across sites and feeds, agents are likely to skip it altogether.
A beautiful webpage matters if humans see it. For agents, clarity and extractability matter far more.
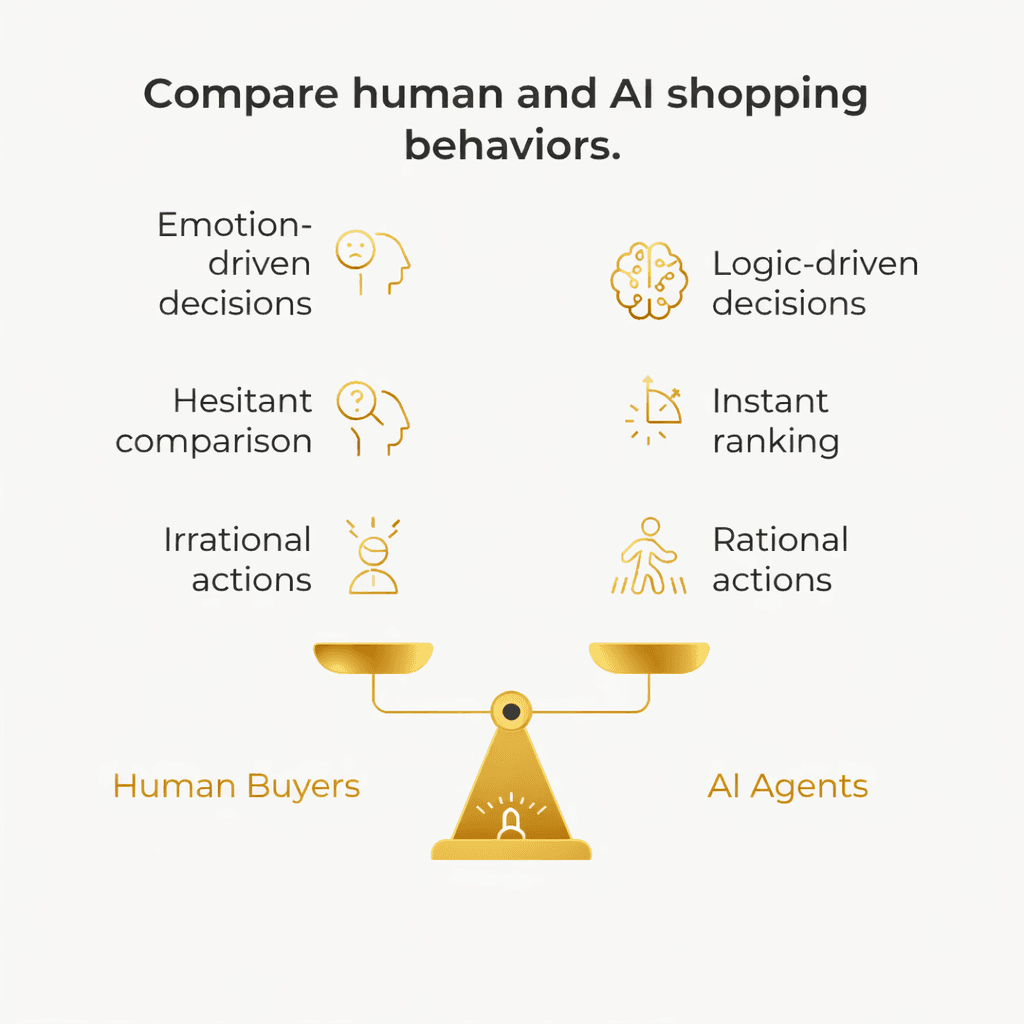
3. Shopping Evaluation: Logic, Not Emotion
Once options are gathered, the agent enters evaluation mode.
Humans weigh emotion, brand affinity, and subjective impression. Agents rely on logic.
They evaluate:
Price thresholds
Feature and specification match
Real-time availability
Return and delivery policies
Trust signals such as reliable citations and updated content
Ambiguous or missing data does not get interpreted. It gets excluded.
Brands now compete in a “logic game” more than a storytelling game.
4. Decision Making: Levels of Autonomy
AI agents vary in autonomy, but there are three broad levels:
Low autonomy
The agent suggests options; a human still decides.
Medium autonomy
The agent filters and recommends; the human confirms.
High autonomy
The agent selects and acts, invoking payments and delivery.
High-autonomy agents do not ask for input once constraints and preferences have been defined. They execute.
This means your data quality and reliability determine whether you even enter the consideration set.
5. Shopping Conversion: Triggering Transactions via Agent Pay
When an agent commits to a purchase, it does not fill out forms or navigate checkout flows like a human.
Instead, conversion happens through:
Agent-powered APIs
These allow agents to trigger actions like initiating carts, booking demos, or submitting checkout requests.
Autonomous payments
Protocols like Visa or Mastercard Agent Pay let agents execute payments on behalf of users within predefined limits and safeguards.
This requires merchants to expose reliable, secure, and auditable systems — not just visually attractive checkout pages.
6. Feedback Loops: Agents Learn and Prioritize
Agents improve over time.
They remember which sources reliably delivered based on criteria like:
Match quality
Transaction success
Delivery timeliness
Return experiences
Brands that consistently perform well in agentic workflows get reused more often, creating a strong feedback loop that reinforces visibility and conversion.
This dynamic mirrors search engine ranking systems but is driven by different signals — logic, reliability, and structural clarity.
7. The New Shopping Optimization Playbook
Traditional ecommerce optimization like keyword SEO and creative ads still matter but are insufficient.
To compete in an AI-driven shopping world, brands must optimize for:
Focus Area | What to Optimize |
Discoverability | Expose structured data via JSON-LD, schema, APIs |
Credibility | Build trust through verifiable metadata and citations |
Clarity | Provide clean, unambiguous pricing, specs, inventory |
Agent Compatibility | Avoid content hidden behind dynamic rendering |
Conversion Readiness | Enable agent-friendly APIs and pay triggers |
This is optimization for logic and structure, not just human persuasion.
Strategic Implications for Leadership
AI shopping agents create two simultaneous pressures:
Upstream visibility risk
If agents cannot parse your data, no human ever sees your offer.
Infrastructure competition
Brands with clear product truth, stable APIs, and execution signals will outperform those competing on design and storytelling alone.
This transition affects:
Product and data teams
Marketing and analytics
Revenue operations
Platform and engineering roadmaps
The cost of doing nothing is invisibility, not just friction.
Where SonicLinker Fits
SonicLinker helps brands observe how AI shopping agents interpret, rank, and act on product data in real shopping environments.
Instead of guessing agent behavior, you get operational insight into where your content succeeds, fails, or gets ignored.
That’s the competitive advantage now.
















